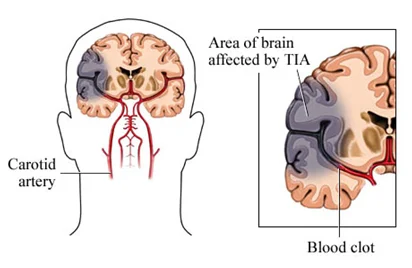
There are two different types of emboli: gaseous or solid.
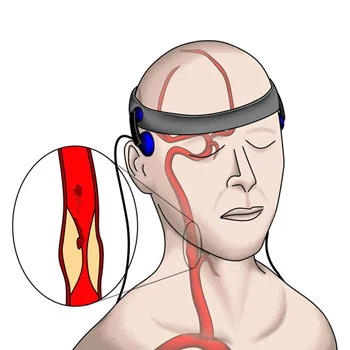
Since cerebral embolism is one of the major causes for ischemic stroke, and due to the fact that the main cause of intraoperative strokes (especially during vascular procedures) is embolism, Transcranial Doppler (TCD) plays a significant role in detecting emboli in patients with carotid atherosclerosis, patients undergoing carotid surgery, and patients undergoing cardiac surgery at all stages of the procedure (pre/intra/post) to significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
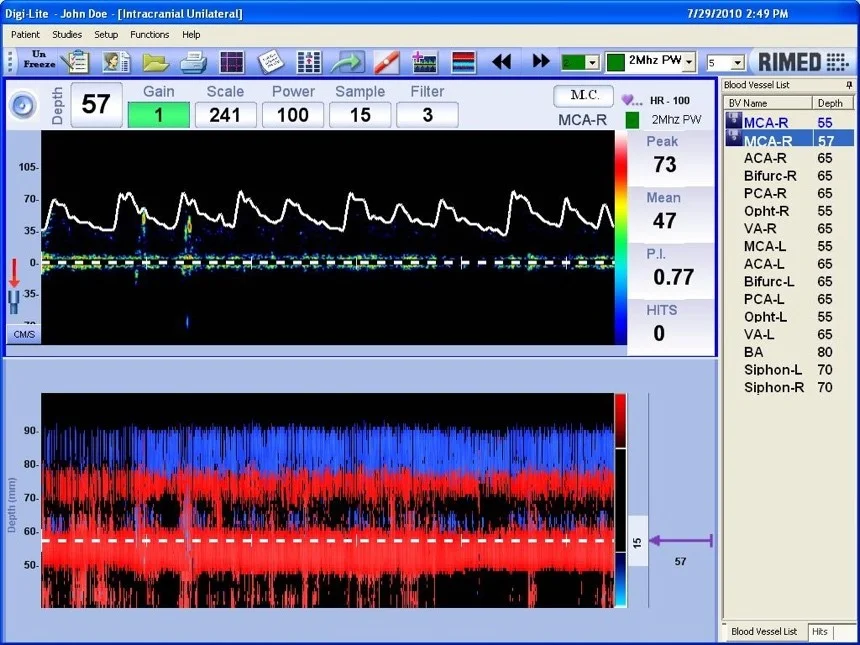
TCD is an efficient tool for emboli detection, as the emboli are detected through a high-intensity transient signal (HITS). These short pattern signals move inside the spectrum in the same direction as the blood flow (as opposed to artifacts) and are usually accompanied by a “chirp,” “snap,” or "moan” sound. Decreasing the gain amplitude and sample volume increases HITS detection and accuracy.
Digi-Lite TCD with its advanced and innovative monitoring and emboli detection software enables highly accurate emboli detection and counting. Its multigate monitoring feature makes it much easier to distinguish between emboli HITS and artifacts and to edit using the built-in post-processing modification feature.